DevOps and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment
""Currently, DevOps is more like a philosophical movement, not yet a precise collection of practices, descriptive or prescriptive.” "
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a culture and set of practices aimed at improving collaboration and communication between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) teams. Traditionally, development and operations teams worked in silos, which often led to delays, bugs, and inefficiencies in software releases. DevOps seeks to break down these barriers, fostering a collaborative environment where both teams work together throughout the entire software lifecycle—from development to deployment and maintenance.
The core principles of DevOps include:
- Collaboration: Dev and Ops teams work closely together, sharing responsibilities and insights.
- Automation: Automating repetitive tasks to reduce manual intervention and speed up the development process.
- Continuous Improvement: Encouraging constant iteration and improvement through feedback loops and regular releases.
What is CI/CD?
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are key practices within DevOps that automate and streamline the process of integrating code changes and deploying software. These methodologies allow development teams to release updates frequently, with minimal errors, and ensure that software is always in a deployable state.
Continuous Integration (CI)
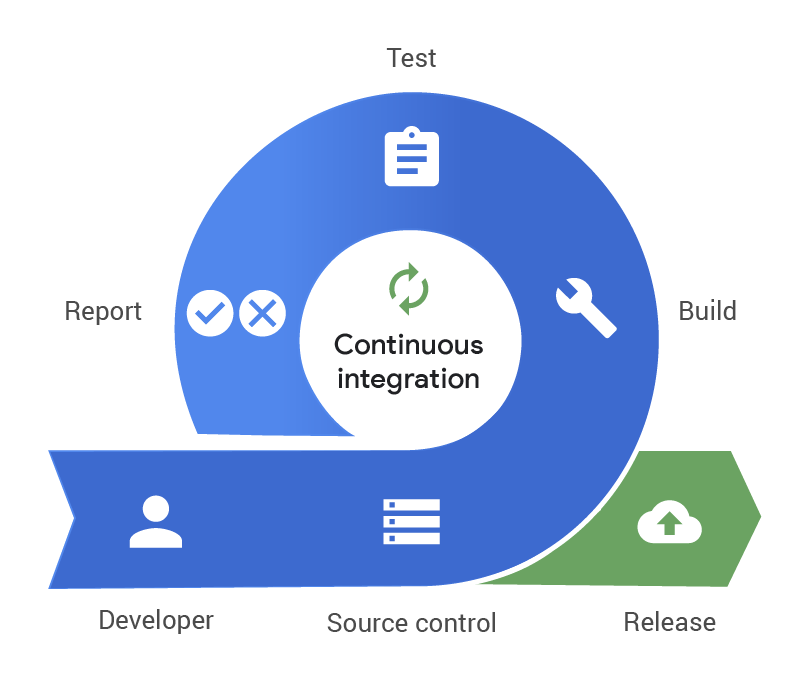
CI is the practice of automatically integrating code changes from multiple contributors into a shared repository several times a day. When developers commit code, automated tests are triggered to ensure the new changes don’t break existing functionality. The goal of CI is to catch errors early in the development process, making it easier and quicker to fix bugs.
Key aspects of CI include:
- Automated Testing: Running tests automatically on each code commit ensures the software is always functioning correctly.
- Frequent Commits: Developers commit smaller, more manageable code changes to the repository multiple times per day.
- Early Error Detection: The frequent integration of code changes helps detect issues before they escalate.
Continuous Deployment (CD)
CD builds on CI by automating the deployment of code to production environments. After the code passes all the tests in CI, it is automatically deployed to production with no manual intervention. This means that once a developer commits a change, it can go live in real-time.
Key benefits of CD include:
- Faster Releases: With automated deployments, new features and updates can be delivered quickly to customers.
- Improved Reliability: Automation reduces human errors, ensuring that the software is deployed correctly every time.
- Faster Feedback: Continuous deployment allows teams to quickly receive feedback from users, improving the product faster.
Why DevOps and CI/CD Matter for Software Companies in 2024
The combination of DevOps and CI/CD helps software companies meet the demands of modern software development and deployment. As organizations face increasing pressure to release new features and updates quickly, these methodologies offer several benefits:
-
Faster Time to Market
By automating repetitive tasks like testing and deployment, DevOps and CI/CD enable software teams to deliver new features and updates more rapidly. This allows companies to respond to market needs and customer feedback faster. -
Improved Collaboration and Communication
DevOps fosters a culture of collaboration, breaking down silos between developers and operations teams. This leads to better communication, faster problem-solving, and more efficient development cycles. -
Higher Quality Software
With automated testing integrated into CI/CD pipelines, software quality improves. Early error detection and frequent testing reduce the chances of bugs reaching production, resulting in higher-quality software. -
Reduced Risk and Downtime
Automated deployment processes reduce the risk of human error during releases, ensuring more stable production environments. CI/CD also allows teams to roll back to previous versions if something goes wrong, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity. -
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
By releasing updates and new features quickly, software companies can address customer needs in a timely manner. Continuous feedback loops also enable teams to adjust and improve the product based on user input, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for Implementing DevOps and CI/CD
Successfully implementing DevOps and CI/CD requires a combination of the right tools, culture, and processes. Here are some best practices to help software companies get started:
- Invest in Automation Tools: Utilize CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and Travis CI to automate testing, integration, and deployment.
- Write Testable Code: Ensure that your code is easy to test. This means writing unit tests and integration tests that can be automated within the CI/CD pipeline.
- Use Version Control: Version control tools like Git allow developers to track changes, collaborate effectively, and manage code releases seamlessly.
- Monitor and Measure: Implement monitoring systems to track the success of deployments and identify issues in real time.
- Start Small: Begin with small, manageable projects to test your DevOps and CI/CD processes, then gradually scale up as your team becomes more comfortable.
